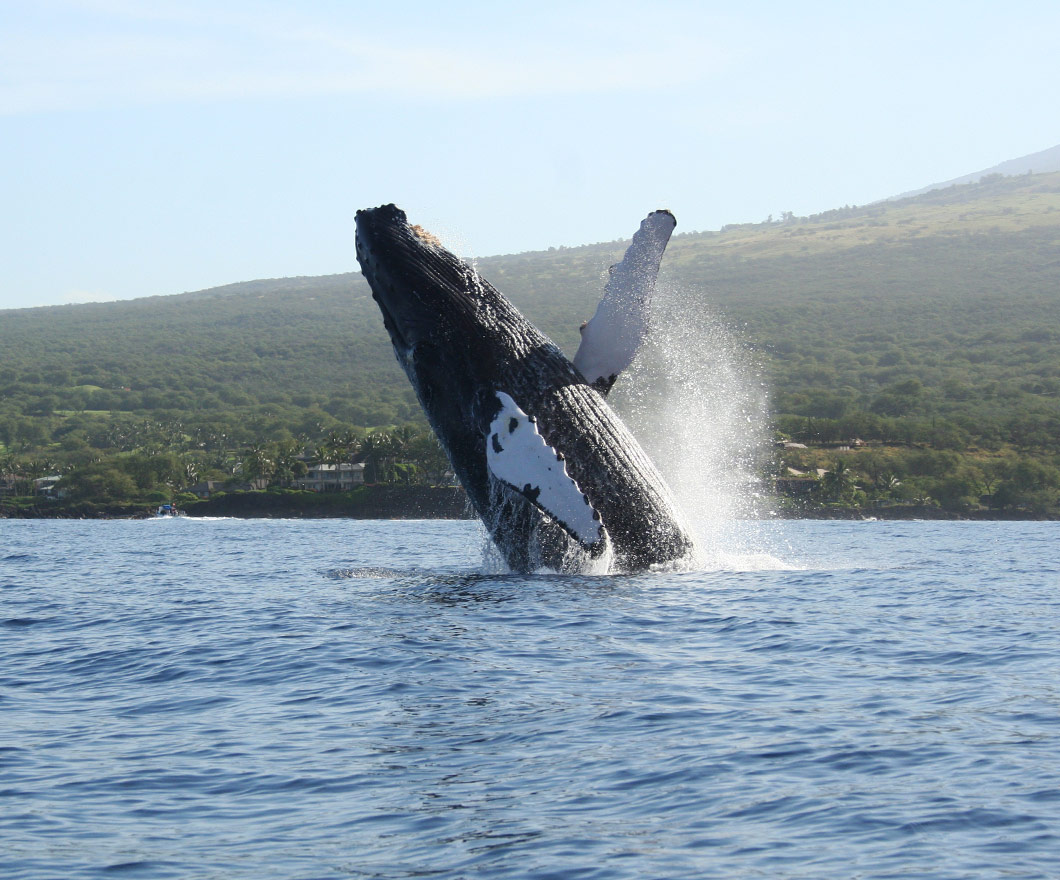
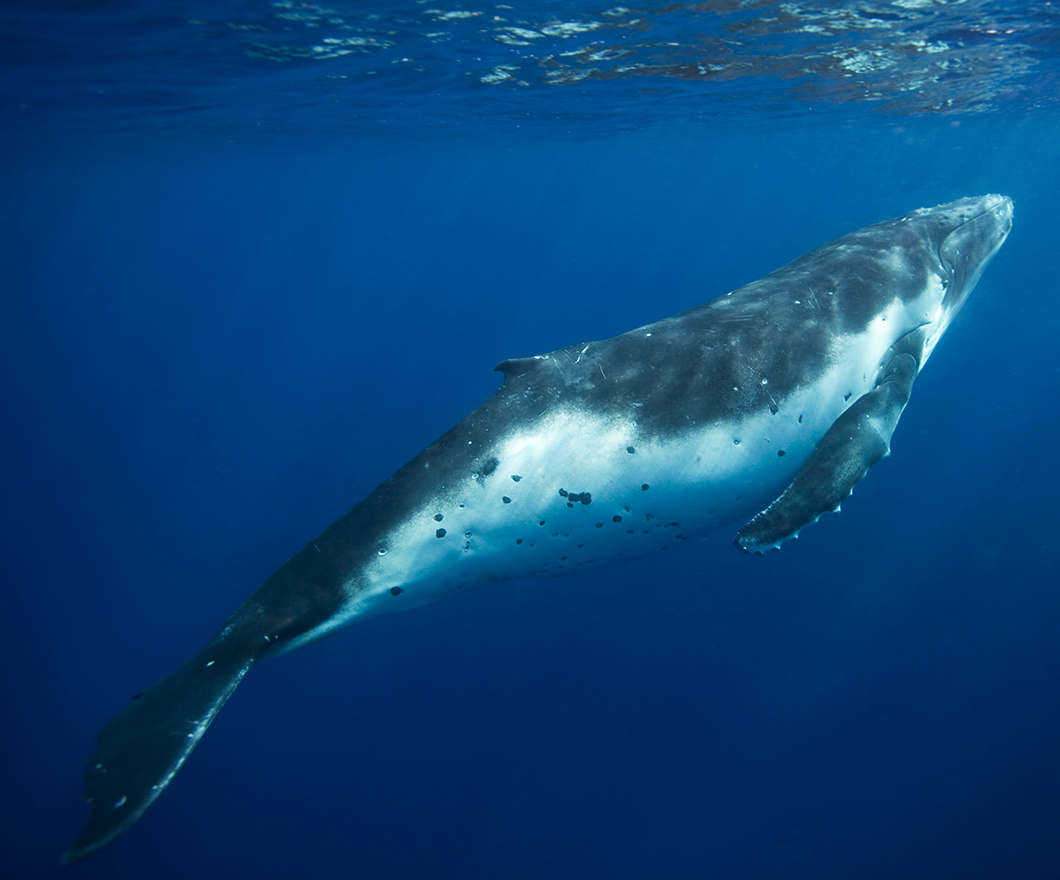
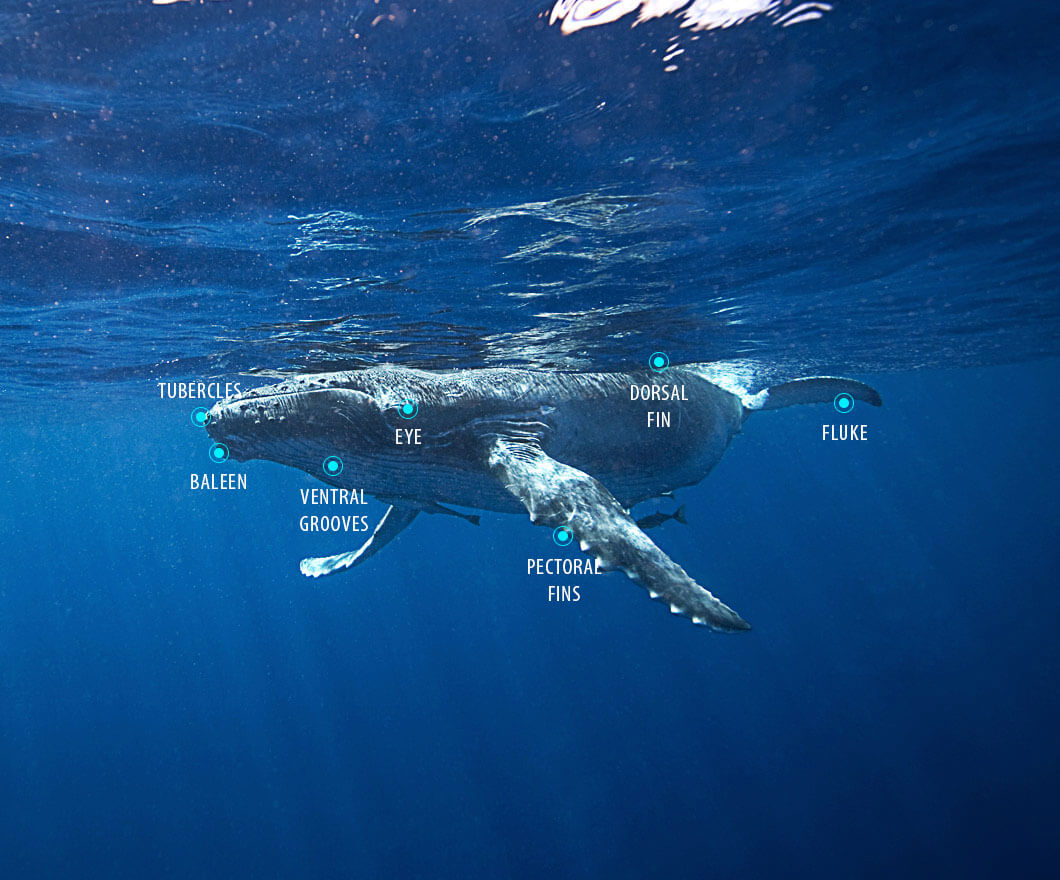
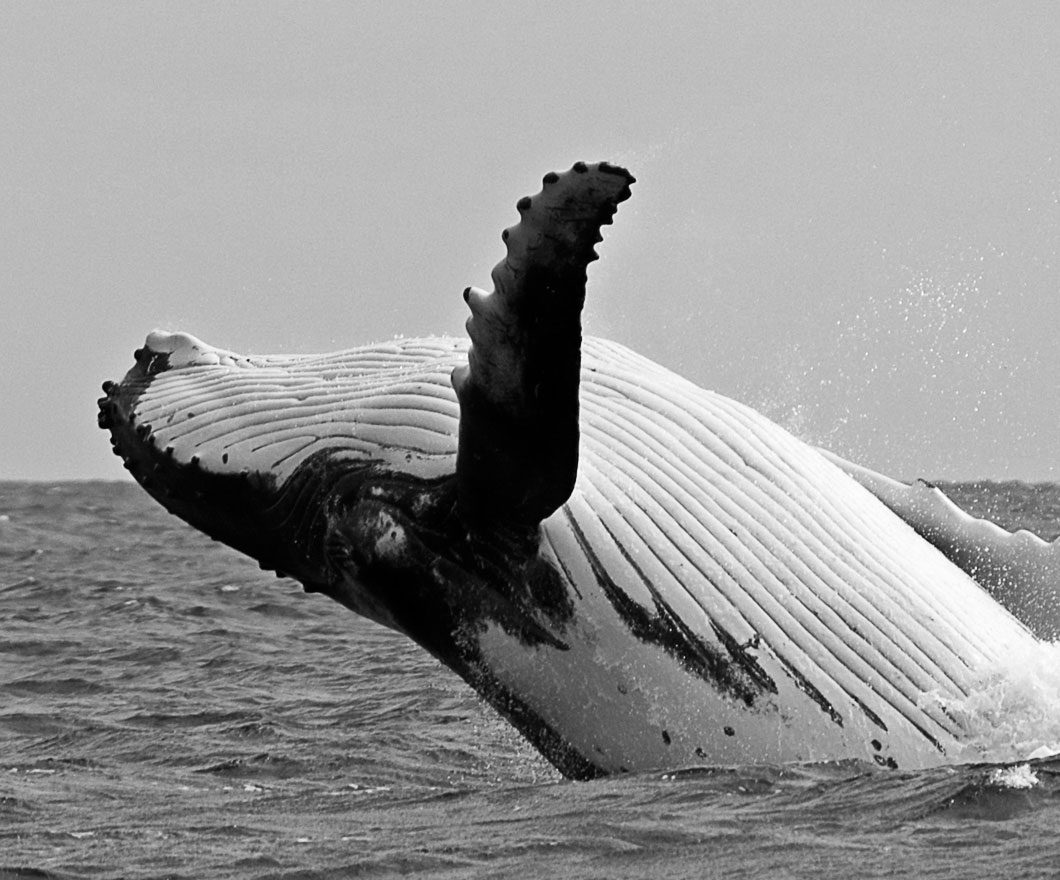
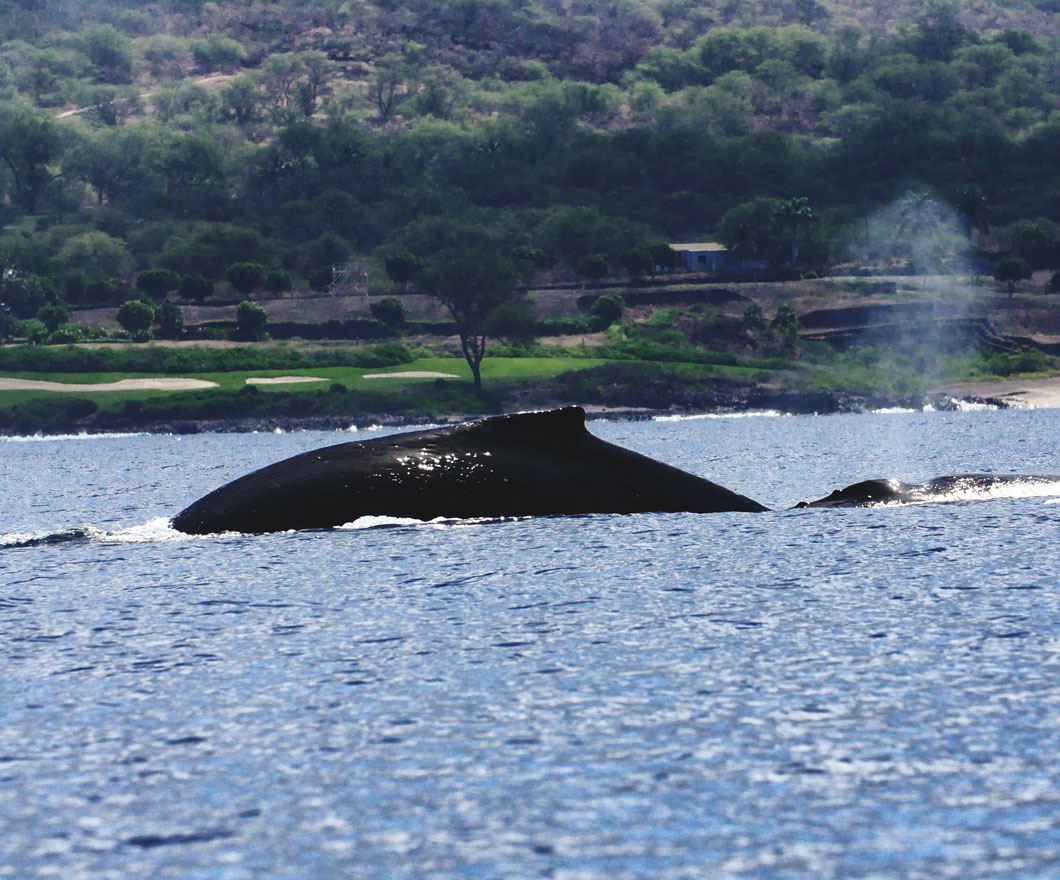
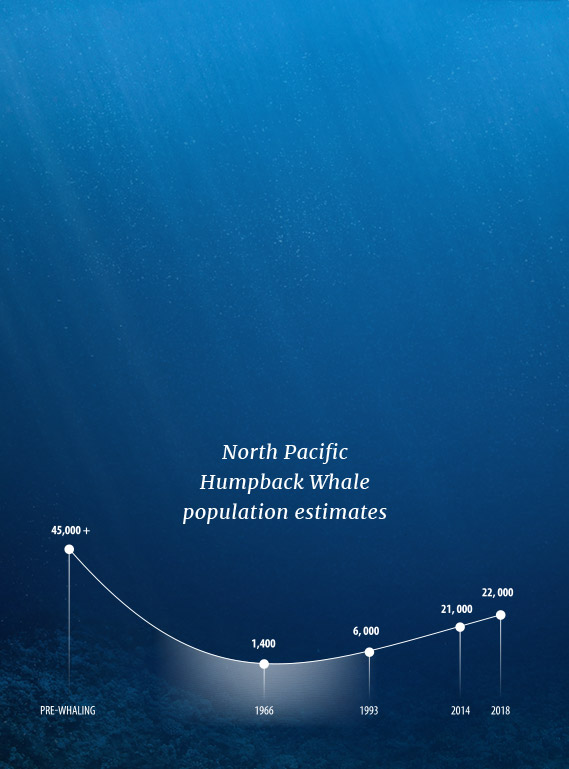
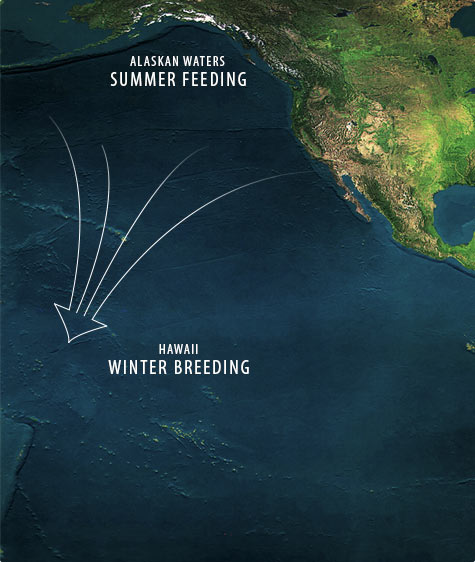
Since the early 1970s, the North Pacific humpback whales (Megaptera novaeangliae) have been under protection by a variety of national and international agreements.
The principal U.S. agreements are the Marine Mammal Protection Act of 1972 (MMPA), the Endangered Species Act of 1973 (ESA) by the NOAA (National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration), and the Convention of International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna And Flora Treaty (CITES) of 1973.
View more